Home — Climate Explorer results: Effects of El Niño and La Niña on world weather: all months
Climate Explorer results
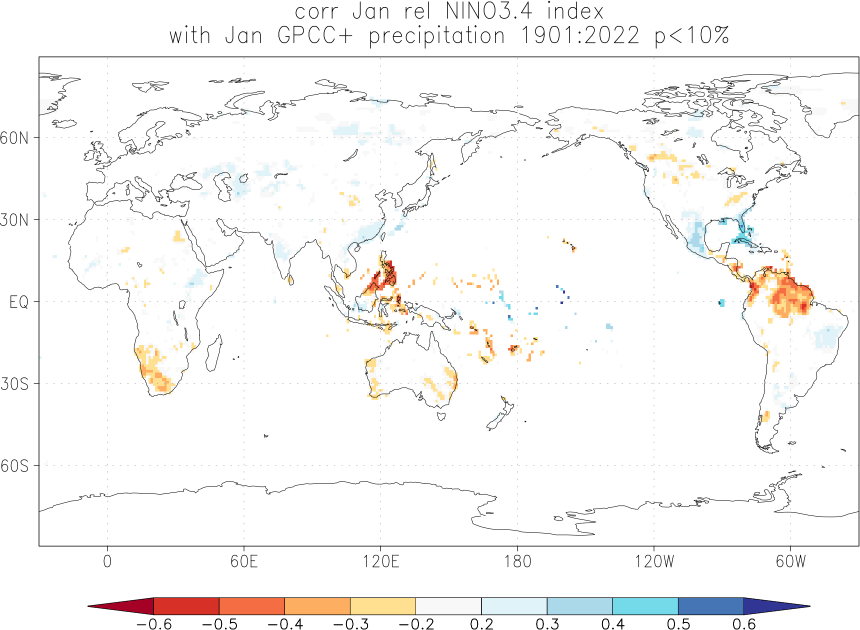
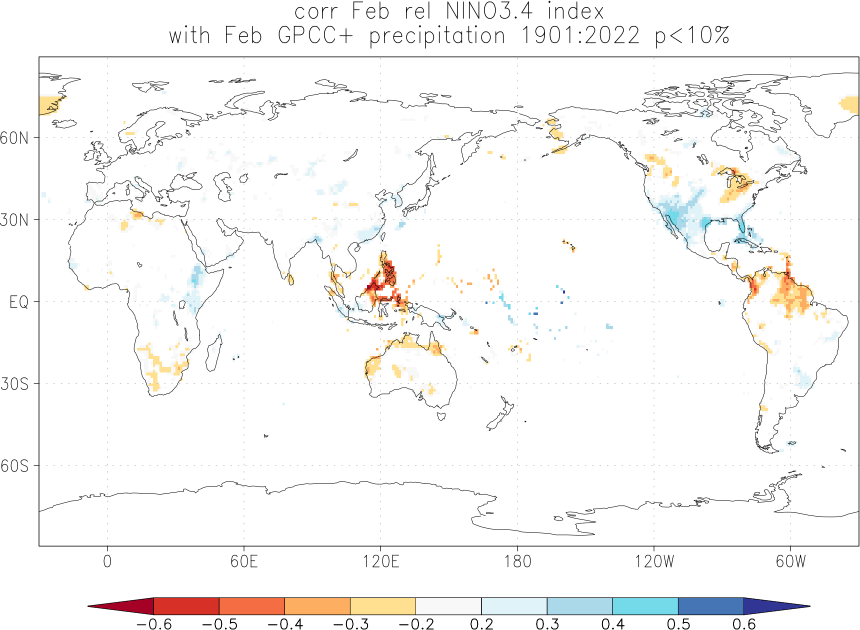
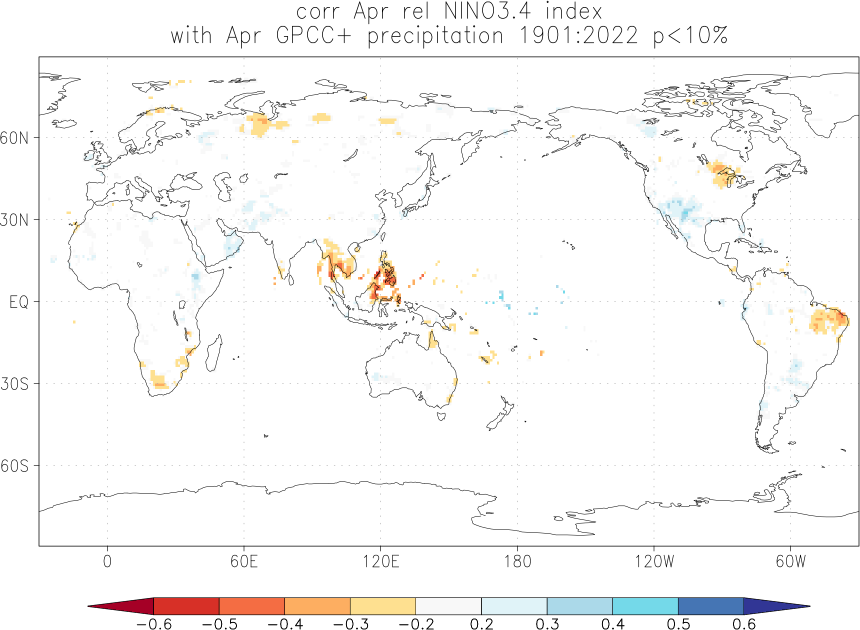
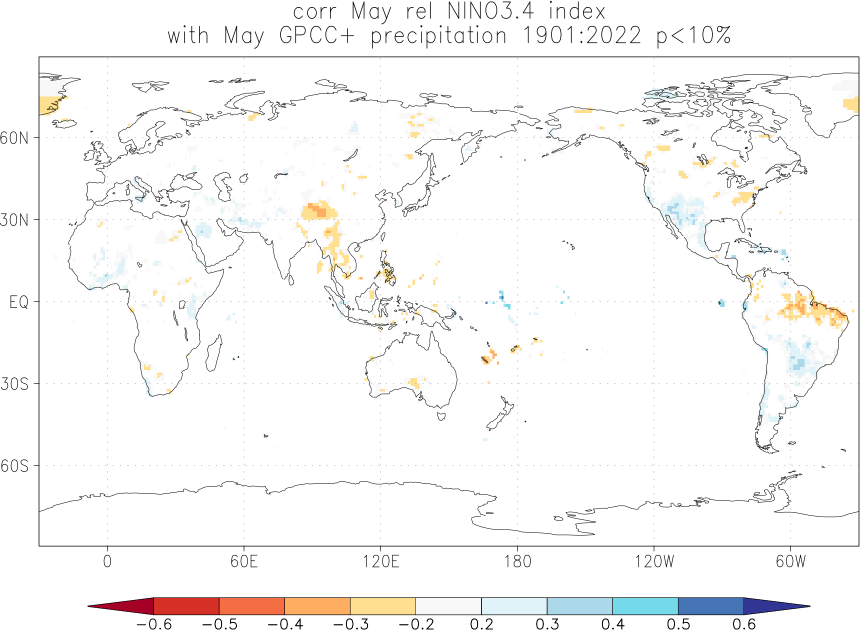
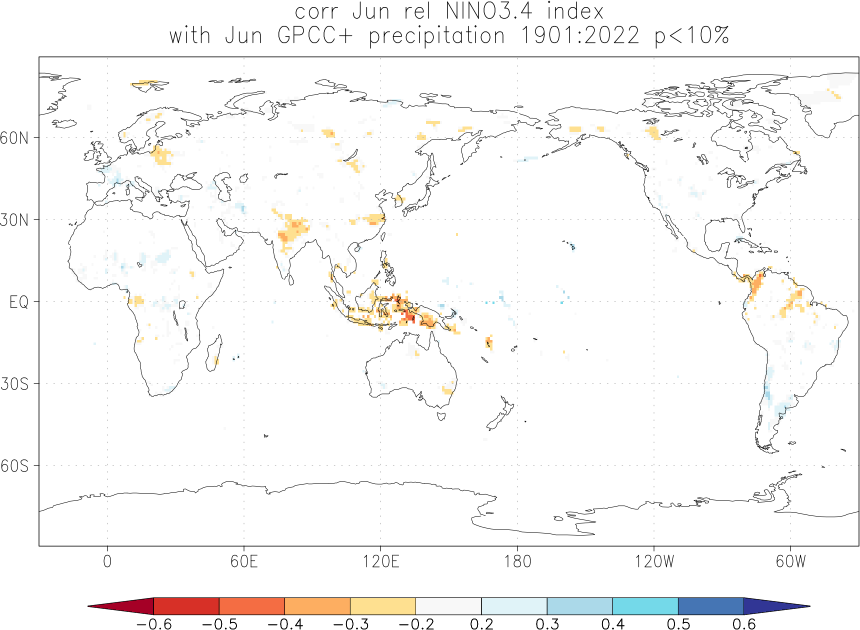
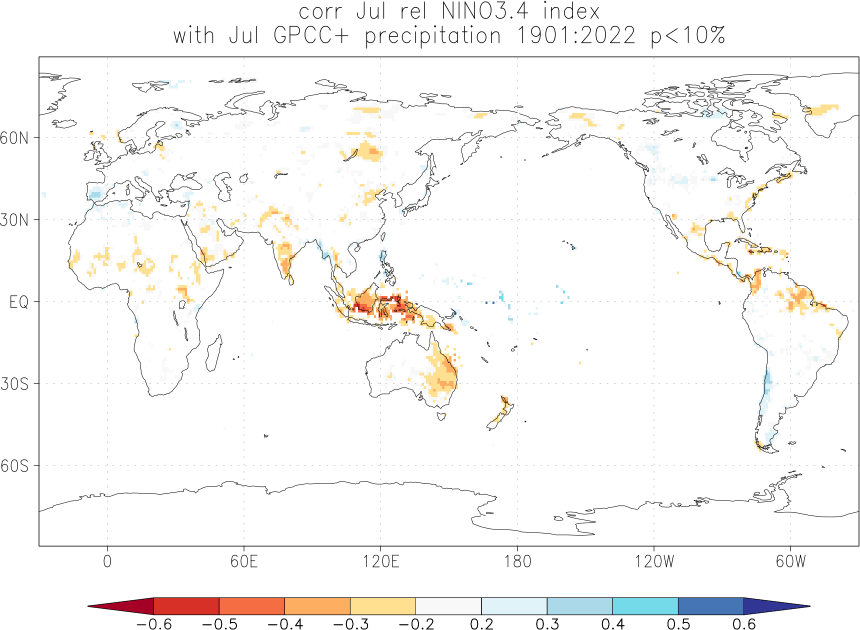
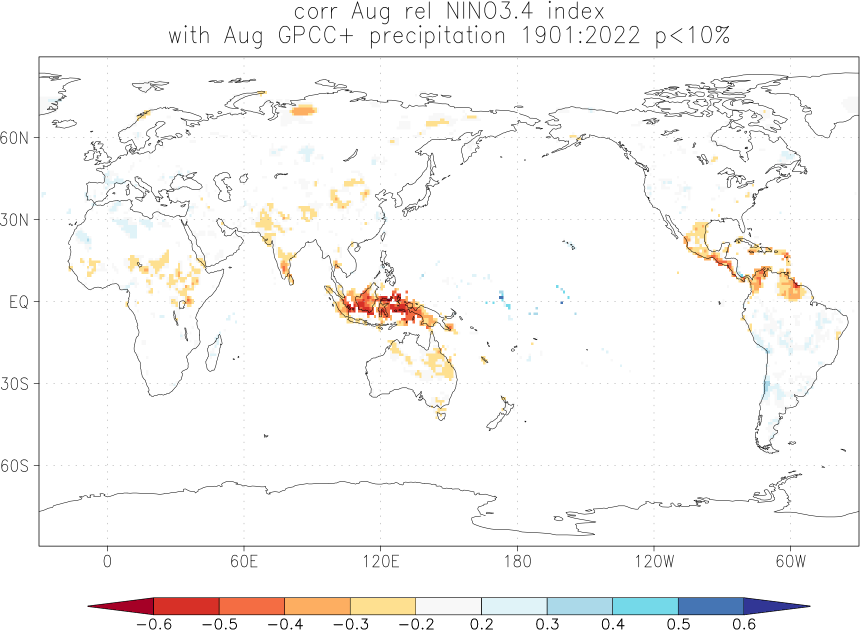
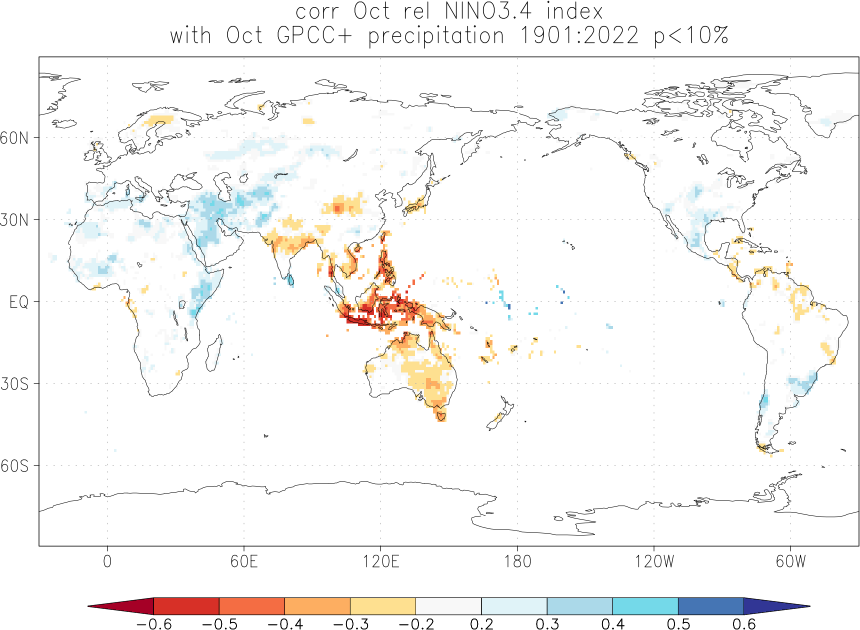
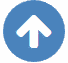
Effects of El Niño and La Niña on world weather: all monthsEl Niño and La Niña affect the weather in large parts of the world. The effects depend strongly on the location and the season. We have studied the GPCC V7 analyses of precipitation over land. White areas did not have enough data. As a measure of the strength of the relationship we used the correlation coefficient with the Niño3.4 index. The square of this number gives the fraction of the variance that is explained by this aspect of El Niño and La Niña.
Blue colours indicate that during El Niño there was, on average, more rain than normal, red colours indicate drought during El Niño. La Niña has the opposite effect in almost all locations.